3 types of muscles:
1) Smooth muscle - controlled by the autonomic nervous system; may either be generally inactive and then respond to neural stimulation or hormones or may be rhythmic. smooth muscles differ the intestines like biceps and triceps because they are voluntary movement.
2) Cardiac muscle - found in the heart, acts like rhythmic smooth muscle, modulated by neural activity and hormones , The most known cardiac muscle is the heart.
3) Skeletal muscle - move us around and responsible for most of our behaviour; most attached to bones at each end via tendons Quads & Hamstrings muscles- are known as the largest muscles in the body, used for balance and everyday activity , as well as posture and supporting body motion Triceps - Arm muscles which contract rapidly, used for bearing loads, and fast reaction movements of the muscles .
- Flexion - contraction of flexor muscles, drawing in of a limb
- Extension - opposite of flexion, produced by contraction of extensor muscles (antigravity
Type 1 - The slow muscles are more used at using oxygen to fuel your day for continuous, extended muscle contractions over a long time. They fire more slowly than fast twitch fibers and can go for a long time before they fatigue. at a low intensity but a long period of time These fibres are used for long distance runners like Mo Farah when Running long distances
Type 2A - The fast twitch fibre is a combination of type 2B and Type 1 and also known as intermediate fast twitch fibres. This would be perfect for a X400m runner due to the event being a sprint but at a further distance as usual.
Type 2B
- Type 2B is a very powerful burst of speed. These fibre has the highest rate of contraction , but can fatigue very easily so it may take a longer rest time to recover. An athlete like Usain bolt would use this Titch fibre when doing his 100 Meters
muscles
Acute responses
- Increase of blood supply : Really depends on the muscles that are being used or needs to be used , for example when playing football a footballer uses mostly his legs. so the blood supply is rushed directly to them. on the other hand when rowing blood is rushed to your upper body to give it enough energy to carry on the task
- Increased pliability : is an increase of a range of movement. For example a footballer who doesn't stretch properly would be at the risk of an injury when playing football. If a footballer stretches properly they would decrease the risk of an injury and would have more of a range of movement.
- Micro tears : During exercise muscles will undergo stress, this will eventually cause micro tears in the muscle fibres. Micro tears are cause by over training a certain muscle to the point of tearing. This is well known in football. This will benefit my athlete because once he suffered from micro tears his muscle will get stronger therefore this will prevent from getting this injury again
Antagonist: The antagonist in a movement refers to the muscles that oppose the agonist. During elbow flexion where the bicep is the agonist, the tricep muscle is the antagonist. While the agonist contracts causing the movement to occur, the antagonist typically relaxes so as not to impede the agonist, as seen in the image above.
The antagonist doesn't always relax though, another function of antagonist muscles can be to slow down or stop a movement. We would see this if the weight involved in the bicep curl was very heavy, when the weight was being lowered from the top position the antagonist tricep muscle would produce a sufficient amount of tension to help control the movement of the weight as it lowers
Synergist: The synergist in a movement is the muscle(s) that stabilises a joint around which movement is occurring, which in turn helps the agonist function effectively. Synergist muscles also help to create the movement. In the bicep curl the synergist muscles are the brachioradialis and brachialis which assist the biceps to create the movement and stabilise the elbow joint.
Synergist: The synergist in a movement is the muscle(s) that stabilises a joint around which movement is occurring, which in turn helps the agonist function effectively. Synergist muscles also help to create the movement. In the bicep curl the synergist muscles are the brachioradialis and brachialis which assist the biceps to create the movement and stabilise the elbow joint.
Fixator: The fixator in a movement is the muscles that stabilises the origin of the agonist and the joint that the origin spans (moves over) in order to help the agonist function most effectively. In the bicep curl this would be the rotator cuff muscles, the ‘guardians of the shoulder joint’. The majority of fixator muscles are found working around the hip and shoulder joints.
Chronic responses
- Tendon strength :
Regular exercise increases tendon density because exercise at high intensity puts a lot of force on the tendon and this increases its strength. This would help a footballer because it will decrease a risk of injury for example of a footballer goes out his way to stretch the ball its less of a chance they will injure their self due to their ligaments being use to the amount of strain.
- Increase of hypertrophy :
Hypertrophy
: This when the muscle increases in size, The methods of muscle size is when a
person works on a particular muscle. This causes nerve impulses which will set
of muscle contraction. This will result to muscle strength and size . This will benefit
the footballer because football is a very physical game ,footballers are always
battling for the ball by barging each other when it’s a 50/50 tackle. Strength
in football separates the men from the boys.
- Myoglobin stores : myoglobin is an iron and oxygen binding protein which is found in the muscle tissue in the vertebrae, mostly found in mammals. However Myoglobin stores increases everytime you exercise because your body gets use to it and the demands your body puts on them .This means it stores more energy.
The energy sytstem
ATP - lactic acid
lactic acid system
- Lactic acid is the breakdown of glucose in the absence of oxygen.
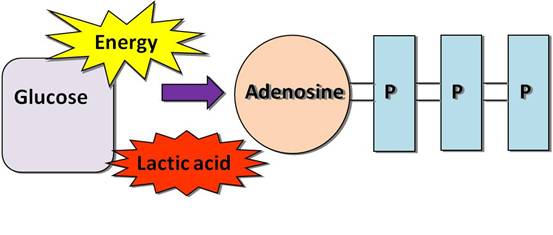 - Takes over when ATP at high intensity for exercise lasting between 2 - 3 minutes
- Takes over when ATP at high intensity for exercise lasting between 2 - 3 minutes- Lactic acid system is used for example a 2 - 3 minute play in basketball because you play a high intensity before resting .
ATP
- ATP stands for Adenosine Triphosphate
- A moleule in the cell that allows for quick and easy access to energy when needed by the cells organelle.
- A type of chemical energy
Aerobic system
- If we want to carry on activity after 3 minutes , the intensity must drop as we cant keep dealing with a increase in lactic acid .
- can break down glucose , glycogen and fat
- vital for stamina in sports such as football and basketball
ATP-PC
The ATP - PC system would be apart of the continuum in the first 8 - 10 seconds of the muscular activity.
short bursts of high intensity exercise, like a 100m sprint may rely almost entirely on anarobic respiration .Energy for sustained periods of exercise. Running long distance like Mo Farah you would be using aerobic respiration. Many different exercise will make you use more then one of the energy system at a time . For example in football or basketball , there are some explosive parts and some low intensity depending on the rate of the game. This may vary depending on the position of the footballer
`
The energy continuum
what is the energy continuum?
The energy continuum is the interaction of the 3 energy systems , this provides energy to the resynthesis ATP. This conveys the same percentage of every system. But this depends on the duration and intensity of the activity you're taking part in.The leading system initially is the ATP/PC as shown in the diagram .as the PC gets exhausted (ATP-PC/Lactic acid threshold the lactic acid system takes over , As said before this may depend on the intensity of the activity.The lactic acid /aerobic threshold is reached between 1 - 3 mins.The aerobic system now becomes the main provider of energy , for ATP synthesis
The characteristics of a 100 M sprinter is split 50% from the ATP-PC system and 50% from the anaerobic glycolysis system, whereas a long distance runner like Mo Farah relies entirely on the aerobic system. However on the other hand , football is a variety of intensities. Short sprints are interspersed with periods of jogging, walking, moderate-paced running and standing still. This kind of activity has been named "maximal intermittent exercise". As an whole when playing football all 3 energy systems would be used depending on the intensity of the game. Different positions on the pitch uses different energy at different times for example , a goal keeper would be standing still using aerobic energy where else a striker could be using lactic acid when sprinting with the ball.In football the most used characteristics is cardiovascular endurance fitness. This is one of the key aspect to play football and majority of other sports. This comes in to play because the athlete should be able to keep up with the rate and levels of this particular sport. It’s not just footballer has to cope a 90 minute high intensity game but has to recover as quick as possible when they have short breaks within the game. For a footballer to have good endurance he must do a lot of training for him/her to improve and get their bodies use to it. Football is a variation of different intensities depending on the rate of the game. Sometimes a player will sprint and sometimes jog or even stop. For example if a players injured and is waiting for assistance the players may stop fully and take a short break ( This will be made up at the end called extra time) The energy system that may be used is lactic acid This energy sytem fuels short burst when a footballer ( striker ) is sprinting for the ball.
